Search
The Proposed I-140 EAD Rule - Continually Updated
This entry is now old law. The new law is at http://www.immigration.com/blogs/i-140-ead-regulations-effective-17-jan…
Note: Updated all of the regulations comments on 31 December 2015. I will keep adding, as needed.
DHS Enhances Opportunities for H-1B1, E-3, CW-1 Nonimmigrants and Certain EB-1 Immigrants, Final Rule Posted
The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) amended its regulations today to improve the programs serving the H-1B1, E-3 and CW-1 nonimmigrant classifications and the EB-1 immigrant classification, and remove unnecessary hurdles that place such workers at a disadvantage when compared to similarly situated workers in other visa classifications.
DHS Enhances Opportunities for H-1B1, E-3, CW-1 Nonimmigrants and Certain EB-1 Immigrants, Final Rule Posted
The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) amended its regulations today to improve the programs serving the H-1B1, E-3 and CW-1 nonimmigrant classifications and the EB-1 immigrant classification, and remove unnecessary hurdles that place such workers at a disadvantage when compared to similarly situated workers in other visa classifications.
US Work and Immigration Options for Foreign Professionals
US Work and Immigration Options for Foreign Professionals
A discussion with two members of our community
E-3 Visa
Overview
The E-3 visa allows for the admission of an alien who is a national of the Commonwealth of Australia and who is entering the U.S. to perform services in a “specialty occupation.” The E-3 visa has many advantages over the other types of working visas, including the ability for spouses of E-3 recipients to apply for work authorization.
Nonimmigrant Visas
Success in responding to a Request for Evidence after filing an E-3 Petition
We assisted in responding to an RFE questioning the employer’s educational requirements for an E-3 (Specialty Occupation Workers from Australia) Petition filed for a software developer position. USCIS sought clarification as to how the position could be a specialty occupation where the employer required a minimum of a bachelor’s degree in business, information systems, computer science or equivalent with related experience.
Nonimmigrant Visas
Agency
Immigration Law
Success in responding to a Request for Evidence after filing an E-3 Petition
We assisted in responding to an RFE questioning the employer’s educational requirements for an E-3 (Specialty Occupation Workers from Australia) Petition filed for a software developer position. USCIS sought clarification as to how the position could be a specialty occupation where the employer required a minimum of a bachelor’s degree in business, information systems, computer science or equivalent with related experience.
USCIS Updates Guidance on Employment Authorization for E and L Nonimmigrant Spouses
Release Date
03/18/2022
U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services is updating guidance in the USCIS Policy Manual to address the documentation that certain E and L nonimmigrant spouses may use as evidence of employment authorization based on their nonimmigrant status.
USCIS Updates Policies to Improve Immigration Services
Release Date
06/09/2021
WASHINGTON—U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services has issued new policy updates in the USCIS Policy Manual to clarify the criteria and circumstances for expedited processing; improve request for evidence (RFE) and notice of intent to deny (NOID) guidance; and increase the validity period for initial and renewal employment authorization documents (EADs) for certain noncitizens with pending adjustment of status applications.
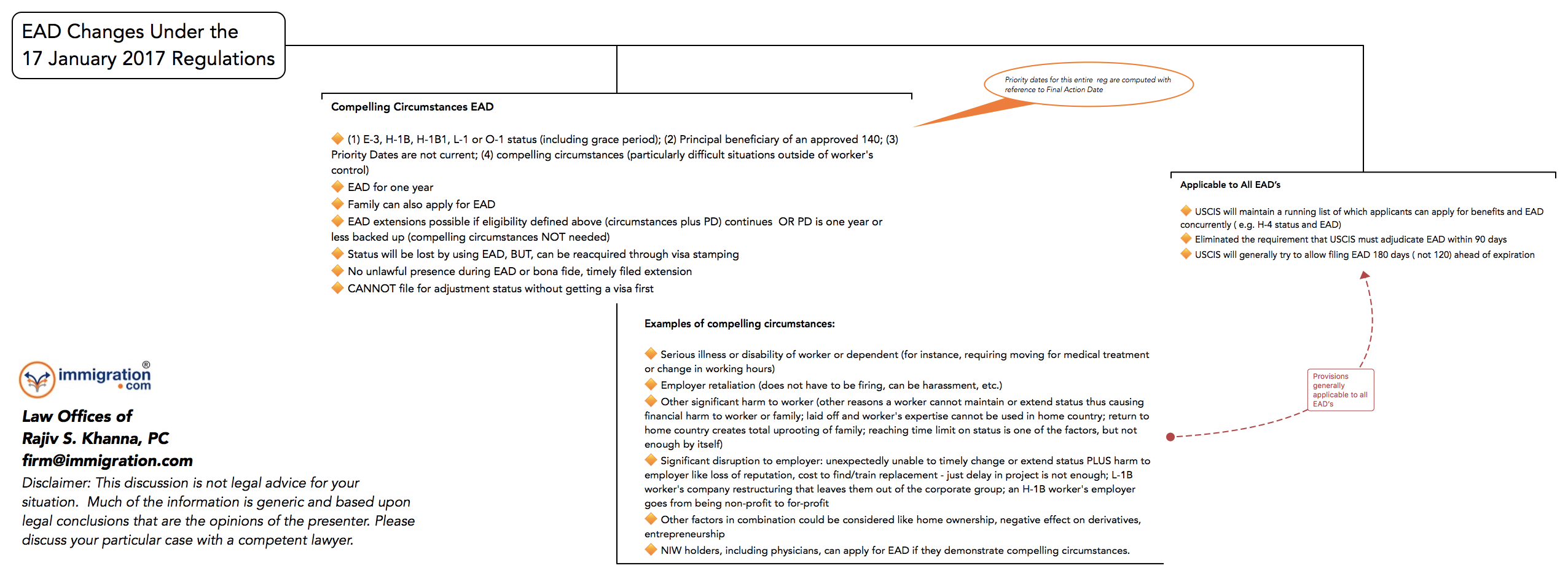
I-140 EAD Regulations Effective 17 January 2017
2 December 2016
Radio Show Discussing Overview of the new I-140 EAD Regulations
2 December 2016
Discussing I-140 EAD FAQ in community conference call
E-3 Visas for Australian Citizens
We were retained by a corporate client to process several E-3 petitions for nationals of Australia. All of the visas were issued at the Australian consulates without any problem. One applicant has already entered the U.S is currently working on E-3 status. We have also submitted a petition for an E-3 amendment with USCIS, which was also approved without any issues.
Nonimmigrant Visas
Profession/Occupation
DOL Publishes FAQs On H-1B, H-1B1 And E-3 Programs
The Department has posted new Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for the H-1B, H-1B1 and E-3 Programs.
Options for Nonimmigrant Workers Following Termination of Employment
Release Date
12/19/2022
U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) is providing information for nonimmigrant workers whose employment has terminated, either voluntarily or involuntarily. These workers may have several options for remaining in the United States in a period of authorized stay based on existing rules and regulations.
May 19, 2023, Rajiv in QnA on behalf of students and young professionals (What is RFE, NOID, NOIR)
Nonimmigrant Visas
Immigration Law
SUBSCRIBE to Immigration.com YouTube Channel for further updates.
Immigration.com, Law Offices of Rajiv S. Khanna PC, US Immigration Attorney Rajiv Khanna
Blog: http://www.immigration.com/blogs
USCIS Provides Guidance on Employment Authorization Documents Based on Compelling Circumstances
Release Date
06/14/2023
U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services today released policy guidance on the eligibility criteria for initial and renewal applications for employment authorization documents (EADs) in compelling circumstances based on existing regulatory requirements at 8 CFR 204.5(p).
For an applicant to be eligible for an initial EAD based on compelling circumstances, they must meet the following eligibility requirements:
Guestbook Entry for A Singh, United States
Guestbook Entry for Dilip K, United States
DOL Issues New FAQ on H-1B, H-1B1 and E-3 Programs
The Department has posted new Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for the H-1B, H-1B1 and E-3 Programs.
To view FAQ please check the attachment.
New H-1B, H-1B1, E-3 Notices from DOL
H-1B, H-1B1, E-3 Helpful Resources:
The Department has posted a contact list for the H-1B, H-1B1 and E-3 Programs to assist employers with their applications. To view or download a PDF copy of the Helpful Resources for the H-1B, H-1B1 and E-3 Programs, please click the attachment below.
Visa denial based upon immigrant intent, Section 214(b) of Immigration and Nationality Act
Nonimmigrant Visas
Immigration Law
Substantial transcription:
7th July 2012 at 05:16 PM
9.59 Minutes
What do we do when our visa gets denied under section 214(b) of the Immigration and Nationality Act? Basically, this means that if the consulate doesn’t believe you are going to come back, they deny the visa, saying that you have an immigrant intent which you have not been able to rebut. So the idea is whenever somebody goes for a visa stamping, they actually are presumed to have immigrant intent unless they prove otherwise. Of all the visas A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H all the way to V, some visas are immune to this problem.
What are the visas that are immune?
H-1 as well as H-4, L-1 as well as L-2, and O-1 and O-1 derivative visas are immune by law almost. H and L are clearly immune by law and O by implication. With these visas, if you have a green card going, the consulate is not going to deny your visa for that reason.
On the other hand, there are notorious visas that are very susceptible to this problem:
B-1, B-2, F-1 as well as F-2 (which are for students), and J-1 as well as J-2 are susceptible. A lot of physicians on J-1’s have had a visa denial on 214(b).
TN visa holders strictly not going for visa stamping but can be stopped at the border if their green card has been filed. So bear in mind that when TN holders apply for a green card, they should be careful about this particular factor.
The biggest problem with 214(b) is it is extremely difficult to fight it. I have recently taken a case in which an F visa was denied on 214(b), and I think we have a fighting chance because the visa applicant has come to the U.S. many times and she has left within her time permitted. So she’s been a frequent traveler on a B visa. Her F visa denial is extremely unjustified, in my opinion.
Let me just very quickly go through the visa alphabets.
A visa (diplomats) will have no problem. They have no issues of a green card being denied.
B visa will have a problem.
C, D, and E visas will usually not have a problem.
The only thing you have to establish for E-3, especially for Australians (E-3 is kind of equivalent of H-1), is that you do have an intention to come back but not to the same degree. In other words, if you have a home in Australia, the degree of proof is not very high so it is very easy to meet that degree of proof.
G visa is ok.
H visa is ok.
By the way, H-2B visas can have a major problem with immigrant intent. These are people who are coming to U.S. for to perform skilled labor.
I, which is international journalists/media representatives, may or may not be ok.
J visa will definitely be a problem.
K -1 and K-3 are no problem because they are fiancés or spouses of U.S. citizens and are obviously meant to go into green card.
L visa is no problem.
M, which is folks who are doing vocational training, can have this problem.
P visa (performers, athletes, etc.) can have a problem but usually won’t.
Q visa (exchange visitors) can have a problem.
R visa usually won’t.
S, T, and U visas won’t usually have a problem because they are done within the USA and are usually either victims of crime or people who are assisting in criminal investigations.
So what do you do if you get a 214(b) denial?
Normally there isn’t much we can do but, if you have been to USA before or else there is something unique in your case, we can ask the consulate to reconsider and if they are not willing and able, then we can ask the visa office in Washington, D.C. to intervene. You can also contact your family or employer in the U.S. to contact the local Congressmen to seek their intervention. This typically is not helpful but you can try. If anybody from the bar or a lawyer tells you he or she can fix it, be mindful because they may not be able to. Especially be careful when you talk with lawyers in your own country. This makes me very nervous because we have had some cases where local lawyers in other countries did some strange stuff. They had some hook ups with consulates and ultimately got caught.
The biggest problem is with fraud or misrepresentation. If you make a misrepresentation in attempting to get any immigration benefit, you can be barred from entering USA forever.
Going back to 214(b) denials, you can ask the consulate to reconsider. Reapply if you have a case that begs for a special consideration, like you’ve been to the U.S. many times. For example, one of my friends asked me that, if his girlfriend is refused a B visa, is it okay to bring the lady in on a K-1 (fiancé visa)? My take is do not use the fiancé visa in lieu of B-1 or B-2 visa, because if you do not have the intention to get married, the government can consider it to be fraud. So make sure you want to get married within 90 days after they enter the U.S.
One more point -- there is a legal fiction created in U.S. immigration law about ties to your home country that says you can overcome 214(b) denial if you have ties to your home country. That in my mind is a legal fiction. To demonstrate ties is very difficult. Of course, if you have family in your home country, that’s a good example of ties but to say you have property, but property can be sold, so I don’t think that’s really ties. Having business is also not really a tie as a business can be sold. Hence demonstrating ties to your home country is usually a difficult thing to do.
This issue has come up several times recently. Feel free to ask me specific questions on the website, in a forum, or on a community conference call.